
We are improving the quality of our lives through technological advancement. But have you ever wondered, how are we able to make continuous improvements that are benefiting mankind? Technology transfer is the reason behind identifying discoveries or inventions that accelerate advancements. In other words, it ensures that the technology in the laboratory is transferred to practical applications across various industries and homes. Now that you roughly know what technology transfer is, let’s take a look at its definition, significance, usefulness, methods, and types.
What is Technology Transfer?
Technology transfer represents a process of transferring knowledge or skills that manifest as technology from the owner to another organization. In this case, the owner can be a person or an organization. The purpose of transferring technologies varies. A few common reasons are commercialization and sharing of knowledge, skills, or manufacturing methods. Broadly speaking, technology transfer is done between government, business, universities, and research and innovation societies. With its help, scientific and technological developments become available to a wider audience.
Importance of Technology Transfer
Undoubtedly, we live in a highly competitive world. One way businesses can get a competitive edge in the market is through innovation. That’s why inventions are the priority of most businesses and technology transfer is a medium to commercialize them. Also, publishing the research doesn’t guarantee that it will be noticed. We need technology transfer to encourage collaboration, which is essential for developing technologies. Additionally, the process of devising technologies is expensive and time-consuming. With union brought through technology transfer, the risks and rewards are shared, eventually making the technology development process attainable.
What are the types of Technology Transfer?
Technology transfer is classified into three types: technology push, market pull, and technological spillover. Let’s explain them.
Type 1. Technology Push
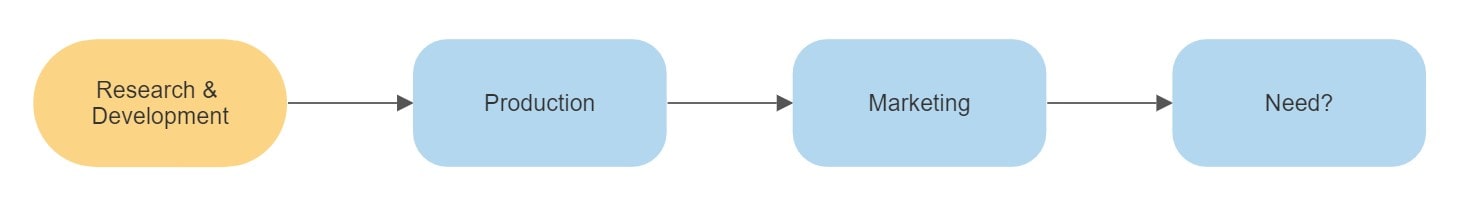
In the technology push approach, the university or company patents its inventions which are then licensed to other companies. Its primary focus is the development of inventions for driving new consumer demands. It doesn’t take into account the market needs, however. The benefit of this approach is that the owners get to roll out their inventions in the market. However, since it is development-focused, some inventions never get to reach it.
Type 2. Market Pull
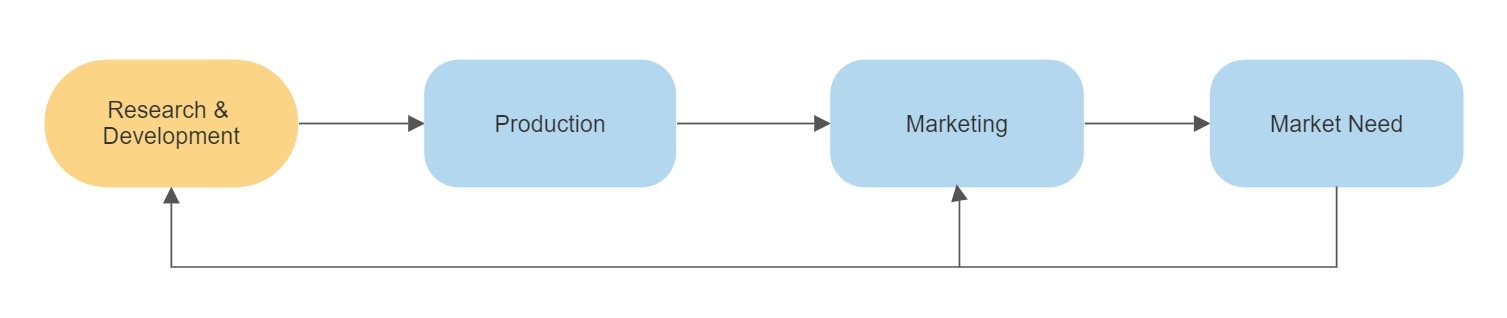
In the market pull type, the innovations are developed in response to customer demands or market forces. The priority of the market pull lies in solving industry problems or market needs. Since innovative solutions are developed for the problems faced in the market, the adoption rate of these technologies is high. They are more likely to be successful as the market opportunity has been validated. Additionally, using this approach, the technologies reach customers quicker and companies get a return on their research investment.
Type 3. Technological Spillover
The third type is technological spillover, where the advancements are made from the research and development efforts of other companies without sharing the costs. In other words, the new advances in one industry simulate the progress in another.
Who Benefits from Technology Transfer?
The advantages of technology transfer are shared among various stakeholders. A few are listed below:
1. Universities
Technology transfer allows universities to improve their research. Alongside that, it improves the prestige of the institution and its scientists and innovations. It provides them with an opportunity to create a positive impact through their academic work. Furthermore, it supports faculty retention and recruitment. It also increases their chances of receiving grant funding while providing them with revenue to support existing and new research activities alike. Not only this, but with technology transfer, universities can develop alliances on ground-breaking research projects.
2. Businesses
Technology transfer gives businesses access to technologies that help them in creating innovative products, services, and in some cases companies. It also provides them with access to the expertise, skills, and opinion of world-leading scientists and engineers. This further helps them in talent development, impactful innovation, and prototype development.
3. Societies
Technology transfer brings innovation and job creation to societies, which aids them in supporting their economy. Consequent technological advancements improve public health greatly. Academic discoveries when put into practical application also benefit the public on a large scale. That not only saves their lives and improves their health, but also provides them with a cleaner environment. The other upsides of technology transfer for societies are community and corporate engagement.
Methods of Technology Transfer
Several methods of technology transfer exist, and some are as follows:
1. Licensing
In this method, the owner of the technology, also known as “the licensor” gives the right of using developed technology to the receiver, also known as “the licensee”. This contract comes in two forms: exclusive and non-exclusive rights. The licensee with exclusive rights can use the developed technology. Whereas the licensee with non-exclusive rights may also transfer the technology to others along with using it.
2. Joint Venture
In a joint venture, two or more companies create an agreement to work together. This includes profits sharing, mutual assets, co-production, risk, and management. While joint venture incorporates long-term cooperation between companies, it takes the ability of independent management away. The common problem in this type of method is differences in the vision and goals of partner companies.
3. Franchising
Companies involved in franchising receive the right to use the trademark and business model of the owner. Additionally, they receive guidance on the operation and management of the franchise technology from the owners. While the franchise gives a company a ready-made brand, it is expected to follow internal rules and procedures set by whoever owns the technology.
4. Foreign Company Acquisition
In this method of technology transfer, the company acquires a foreign company developing new technology. From the acquisition, the company not only gets the technology but also a capable team developing it. However, the key employees’ resignations after the purchase can be a major risk with this technology transfer method.
5. Buy-Back Contracts
Foreign companies that employ buy-back contracts supply equipment to local companies in exchange for the profits derived from the products or services produced using that equipment. The usefulness of this method is that the local companies get advanced technology without investing in it directly.