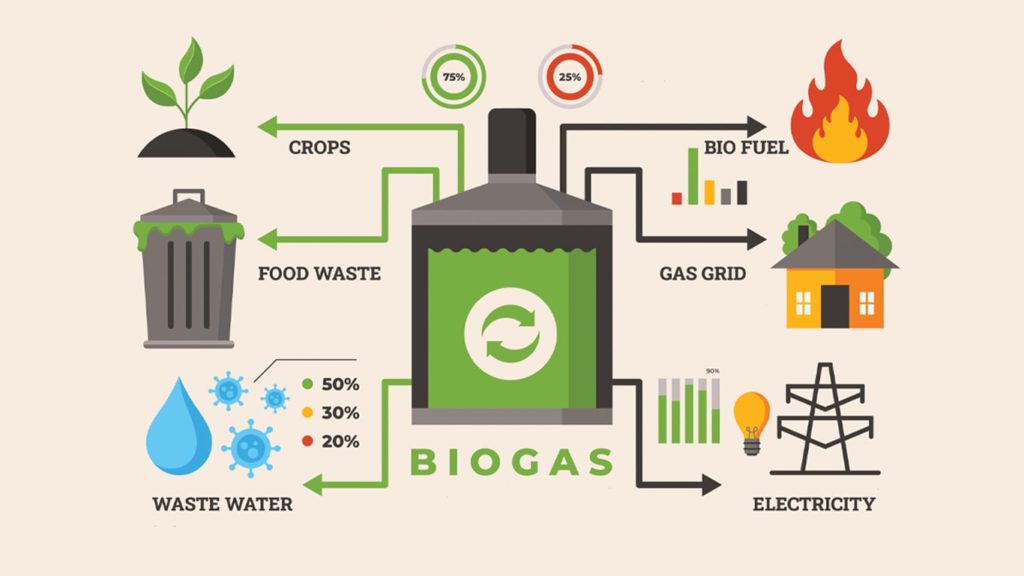
Protecting the environment has become our priority due to the major issues that we are currently facing. Global warming, ozone layer depletion, pollution, and natural resource depletion are a few of the challenges. We want to use the pros of renewable sources of energy to reduce pollution and conserve natural resources. That’s when biogas and its definition come into the picture. It is renewable energy produced through anaerobic digestion unlike fossil fuels created through geological processes.
Biogas is used as a fuel for generating electricity using a combustion engine. It is also utilized for combined heat and power operations. Now that you have an overview of the topic, let’s understand its definition, production, benefits, and environmental impact in depth in the following section. Also, you can check our previous post on the advantages and disadvantages of biogas.
What is Biogas?
Biogas is a type of biofuel produced naturally through the decomposition of organic matter. These organic matters can be food scraps, animal manure, field waste, animal waste, biodegradable waste by-products, or sludge from wastewater treatment plants. These organic matters are placed inside the fermentor for the production of biogas.

The biogas is used for cooking and indoor lighting at homes. Additionally, it has applications in gas turbines, space and water heating, and absorption heating and cooling. As we have mentioned earlier, it is also used for electricity production.
Alongside this, it can be used for steam production provided that it is cleaned up to adequate standards. While the energy demand of the world is increasing, using biogas is a small yet powerful attempt at scaling up the use of renewable energy sources.
How is Biogas Produced?
For the production of the biogas, the organic matters are crushed into smaller pieces and slurried. This step is taken to prepare the bio waste materials for anaerobic digestion. In this digestion process, the organic matter is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen.
Also, the organic waste is heated as the microorganism requires warm conditions to decompose them into gases. This process takes place in an anaerobic digester that includes the feedstock source holder, digestion tank, heat exchangers, and the biogas recovery unit.
The composition of biogas includes 55-80% methane, 20-40% carbon dioxide, and trace gases. Methane has a high energy content and through biogas production, instead of letting it escape into the atmosphere, its energy is harvested. Methane contributes to climate change, so through combustion, it is converted to heat and carbon dioxide. Therefore, biogas production reduces the impact of methane on climate change.
Why Choose Biogas?
There are several reasons for picking biogas, among them the top three below:
1. Renewable Resource
Biogas is used as an alternative to natural gas. The extraction process of natural gas causes damage to the landscapes and ecosystem, thus emphasizing the need for sustainable alternatives.
Biogas production is a more sustainable option that utilizes the existing materials that otherwise go to waste. Also, humans and animals will keep producing organic waste, making biogas a renewable source of energy. Furthermore, its production reduces the dependency on foreign countries for importing oil. Not only this, it lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Waste Recycling
Millions of tons of animal, food, and water waste are produced globally. The biogas system is a smart way of utilizing that waste for its generation. Firstly, it manages millions of tons of waste. Secondly, it prevents emissions from entering the atmosphere. Lastly, it provides a natural way of creating healthier soils.
Producing biogas prevents the resources from getting lost. Also, when the abundant supply of waste is left untreated, it leads to nitrogen pollution and runs off into water resources.
Additionally, biogas systems recycle the nutrients in the food supply. That way, the need for using petrochemical fertilizers decreases as there is a natural alternative that makes the soil healthier.
3. Cost-effective
The biogas system is easy to set up and requires low investment on a small scale. Also, the technology involved in its generation is quite cheap. Organic waste is easily available, further simplifying the process of utilizing digesters. Along with being cost-effective, biogas production paves a path for revenue generation.
For instance, the waste treatment facility can create a new revenue stream. Additionally, farmers, industries, and dairies can convert the cost of waste management into profits. It creates employment opportunities and supports the economic growth of the region.
Environmental Impact of Biogas
Along with renewability, waste recycling, and cost-effectiveness, biogas also offers environmental benefits. Since you know the definition of biogas, the positive effects on the environment won’t surprise you.
1. Reduced Deforestation
By using organic waste, the need to consume firewood can be replaced. Rural household uses dead wood for heat generation and cooking, but if it’s unavailable, they harvest live trees. This leads to the destruction of natural forests unless they’re replanted. The organic matter can be fed into a digester to produce biofuels as an alternative to firewood, thereby lowering deforestation.
2. Lower Emission of Greenhouse Gases
Replacing fossil fuels with biogas results in lower carbon dioxide emissions. Methane is the primary component of both fossil fuels and biogas. Therefore, biogas can be used for various applications including cooking, electricity generation, heating, steam production, and pipeline gas.
Biogas represents a carbon-neutral fuel source. This is because the carbon dioxide produced through biogas comes from organic matter. It is the same plant matter that fixed the carbon occurring in the atmosphere. Biogas is a sustainable energy source that can help us fight climate change.
3. Improved Soil Fertility
The benefits of biogas are not limited to reducing greenhouse emissions, they also improve the fertility of the soil. Biogas does so by replenishing the organic material in the ground. The digestate from the biogas plant returns the nutrients to the soil, further enhancing its fertility. This digestate includes phosphorous, an important nutrient that needs to be replenished.
The other benefits of biogas production are proper segregation and recycling of waste that improves sanitation, and thereby the quality of life on earth.
Comparing Biogas with Other Fuels
We all know that there are other fuel or energy sources available. So, how does biogas stand among these? The following table compares biogas with other fuels:
| Factor | Biogas | Natural Gas | Diesel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Organic waste | Fossil Fuel Extraction | Petroleum |
| Composition | Methane and Carbon dioxide | Methane, Ethane, and Propane | Hydrocarbons |
| Type | Renewable | Non-renewable | Non-renewable |
| Carbon Emission | Low | Moderate | High |
| Sustainability | High | Low | Low |
| Energy | Moderate | High | High |
| Use | Heating, Electricity | Heating, Electricity | Transportation |
Is Biogas a Green energy source?
Yes, biogas is a green energy source. In fact, in recent years, it has been considered much more green than other fuels that are available. It is due to the phenomenon that methane is created due to the anaerobic decomposition of organic waste such as landfills, animal manure, or food waste. Thus, it is not only a better way to handle waste but also a convenient energy source.

While there are many who do not believe biogas to be that beneficial for the environment, results have shown that this is not true. In fact, biogas is much more sustainable than the natural gas that we get from fracking, a process that forces rock formation breakdowns. Fracking has been known to be much more harmful to ecosystems and landscapes.
On the other hand, we have biogas, which is a similar fuel to natural gas, but we do not have to destroy anything to get it. We can even utilize materials that are already existing, such as waste landfills, to generate biogas, which is much more profitable for our globe.
Problems of Biogas
Despite its numerous benefits, biogas does have some challenges it has to overcome before it can become mainstream. Similarly, it has a few disadvantages. The following are the problems of Biogas:
- Biogas remains an impure source of energy even after multiple purification efforts.
- It currently cannot be used for large-scale production.
- It is a highly inflammable gas that is prone to explosion due to oxygen and methane, making logistics a nightmare.
- The technology surrounding biogas has yet to see any major breakthroughs.
- Due to the danger it poses, it is currently unsuitable for dense metropolitan areas.