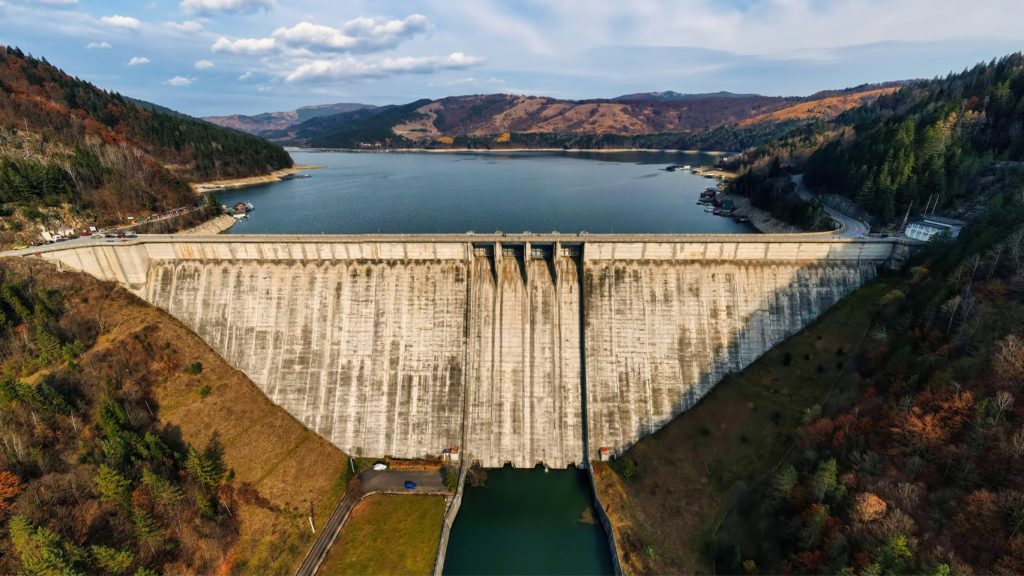

Did you know the world’s first dam is known to be the Jawa Dam, located in present-day Jordan? It was originally built in the 4th century B.C.E, perhaps by the Mesopotamians, some of the first humans to build dams. Earlier, materials such as rocks or clays were used in dam construction. In modern times, mostly concrete is used instead. There are several reasons why dams are built, including three primary ones such as water storage, electricity generation, and flood control. Through them, the reservoirs are created which can then be used for industry, farming, and household applications. Now that you have a brief overview, let’s jump straight to the advantages and disadvantages of dams.
What is a dam?
A dam is a barrier that’s constructed to hold back water and raise its level. Picture this: a massive wall standing tall against a raging river, mastering one of nature’s most powerful elements. That’s your dam. It’s not just about blocking water, though. Dams are like multi-tasking superheroes—they control water flow, make rivers navigable, and even help us have fun with water sports in the reservoirs they create.
Dams come in various shapes and sizes, each with its own personality. You’ve got your simple earth dams, your high-tech concrete arch-gravity dams, and everything in between. The choice of style depends on lots of things—where it’s going to be built, what job it needs to do, and what we’ve got on hand to build it.
Now, operating a dam isn’t as simple as flipping a switch. It’s all about managing spillways, gates, and valves—sort of like running a water orchestra—to keep the water levels and flow just right. Keeping everything in check is super important, ’cause a broken dam? Not a pretty picture.
But hey, it’s not just about the nitty-gritty technical stuff. Dams are also about our relationship with Mother Nature. They’re proof of how smart we are—how we can shape the environment to suit our needs. But they also show us that we’ve got a responsibility to keep things balanced, to look after our planet while we’re using its resources.
Advantages of dams
The water from the dam is extracted, adequately treated, and used by people in the vicinity for drinking purposes. Some other benefits of dams are as follows.
1. They help us store water
Dams help us to build water storage. This stored water can then be used for various purposes including domestic industry and irrigation. Everyday activities such as drinking, cooking, bathing, washing, and watering gardens are part of the domestic use facilitated through dams. The industry uses dams for generating electric power and improving river navigation.
Lastly, they provide a water supply for irrigation that enhances food production. In other words, people can rely on dams to supply water even in drought.
2. Dams control floods
For centuries people have been building dams to prevent floods. The unpredictable floods need to be controlled otherwise it results in massive loss of lives and property. The dams capture the flood water into the reservoir.
That way, the flow is controlled, allowing for proper storage and release of water in supervised conditions. It not only saves human settlements in the nearby areas but also the crops from unanticipated damage.
3. They provide a stable navigation system
The ships travel through water, but if the river is unnavigable, the journey will be affected. That’s when dams are built to provide a stable river navigation system. This way, the depth of water can be maintained yearly, allowing boats and ships to transport goods.
In the absence of dams, the depth of the river may be uneven because of the changing weather, therefore making it unsuitable for water transportation.
4. Dams generate electricity
One efficient way of generating electricity is by constructing dams. The kinetic energy of the downstream water turns the turbine, where its mechanical energy gets converted into electricity. That’s how dams are utilized to provide electricity to nearby houses and industries. It is eco-friendly and fulfills the power needs of both domestic and industrial purposes.
5. They offer recreational opportunities
Dams are not only used for yielding hydroelectric power and supporting irrigation systems, but also for recreational activities. This includes creating reservoirs for fishing. It is especially useful in summer when people can go swimming, camping, boating, and hiking.
Not only this, the dam controllers release water for rafting, allowing rafters to hone their skills. Reservoirs may also have picnic areas near the water, offering recreational access to people.
Disadvantages of dams
Despite all the positives that dams have to offer, their downsides cannot be neglected. The following are some drawbacks dams have.
1. They displace the population
Even though dams are formed with the intention of improving the livelihood of people, the process itself displaces a huge population from the selected area. The formed reservoirs are huge and flood the area, making it unfavorable to live and work. This leads to the breaking up of existing communities as they relocate to a new location to set up their life.
Plus, they may not have the land for agricultural activities, forcing them to develop new skills for their livelihood.
2. Dams are expensive
According to a study at Oxford University, it has been found that the construction of large dams is quite expensive and takes up several resources and years to complete. Considering the amount of money that goes in, the costs are too high to deliver a positive return. Thus, the long period it takes to build dams makes it ineffective for solving urgent energy crises.
Additionally, along with construction, various aspects such as technical and engineering are involved that require absolute precision. Therefore, it is argued that these resources can be put to better use instead of constructing dams.
3. They disrupt the local ecosystem
The construction of dams alters the environment of the surrounding areas. The reservoirs not only disrupt human settlements but also have a negative impact on wildlife. Also, while some plants and animals may adapt to the changing environment, most of them won’t. Therefore, the local ecosystem will be destroyed in the new environment.
Furthermore, the migratory fish are highly affected as they require the unobstructed flow of the river which is now controlled by dam construction.
4. Dams are at risk of flooding
Throughout history, we have seen many cases of dam failures. That’s why several factors are taken into account while constructing them. However, they are still at risk of flooding. Slight neglect in the construction process results in huge losses of lives.
For instance, in 1963, the Vajont Dam outside of Italy failed only 4 years after its construction. The catastrophe resulted in the death of almost 2,000 people. The failure was associated with the location of the dam in a geologically unstable area.
5. They lead to higher greenhouse gas emissions
The dams destroy the local ecosystem along with the vegetation. The decomposing plant matter in the reservoirs produces methane, the greenhouse gas. It is released into the environment and contributes to climate change.
In recent times, several studies have highlighted the contribution of hydropower plants to global warming. It has been found that the reservoirs with more algae and nutrient-rich systems emit more methane. Additionally, the construction of dams results in deforestation. The trees store carbon dioxide, and when they are cut down, it is released back into the environment. To summarize, the construction of dams leads to higher greenhouse gas emissions.
Summary
First, the perks. Dams are like the Swiss Army knives of water management. They hold onto water for us so we can use it when we need it—super helpful in drought-prone areas. Plus, they help create hydroelectric power, a clean and renewable source of energy that’s pretty awesome for our planet. Not to mention, dams keep rivers navigable, which means boats can get around easier. And let’s not forget about recreation—those reservoirs make for some top-notch fishing, swimming, and boating spots.
But then, there’s the other side of the coin. While dams do a lot of great things, they’re not without their downsides. Building a dam is a massive project—huge costs upfront, and you’ve got to have the right spot to put it. Once a dam is up, it can seriously mess with the ecosystem. Think about the fish that can’t swim upstream anymore or the plants and animals whose habits get flooded. They’re also risky—when things go wrong with a dam, they go very wrong. We’re talking catastrophic flooding and serious damage.
So, just like anything else, dams come with their own set of pros and cons. But whether we love ’em or hate ’em, one thing’s for sure—they play a critical role in how we manage and use one of our most precious resources: water.